ARTICLES ON HUMAN ANATOMY, BONES OF THE UPPERLIMB (METACARPALS)
INTRODUCTION
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are equivalent to the metatarsal bones in the foot.
Structure
The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of
distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the
thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter
and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index
metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal
articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others.
The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic
interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is
somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.
Each metacarpal bone consists of a body or shaft, and two extremities: the head at the distal or digital end (near the fingers), and the base at the proximal or carpal end (close to the wrist).

Body
The body (shaft) is prismoid in form, and curved, so as
to be convex in the longitudinal direction behind, concave in front. It
presents three surfaces: medial, lateral, and dorsal.
- The medial and lateral surfaces are concave, for the attachment of the interosseus muscles, and separated from one another by a prominent anterior ridge.
- The dorsal surface presents in its distal two-thirds a smooth, triangular, flattened area which is covered in by the tendons of the extensor muscles. This surface is bounded by two lines, which commence in small tubercles situated on either side of the digital extremity, and, passing upward, converge and meet some distance above the center of the bone and form a ridge which runs along the rest of the dorsal surface to the carpal extremity. This ridge separates two sloping surfaces for the attachment of the interossei dorsales.
- To the tubercles on the digital extremities are attached the collateral ligaments of the metacarpophalangeal joints.

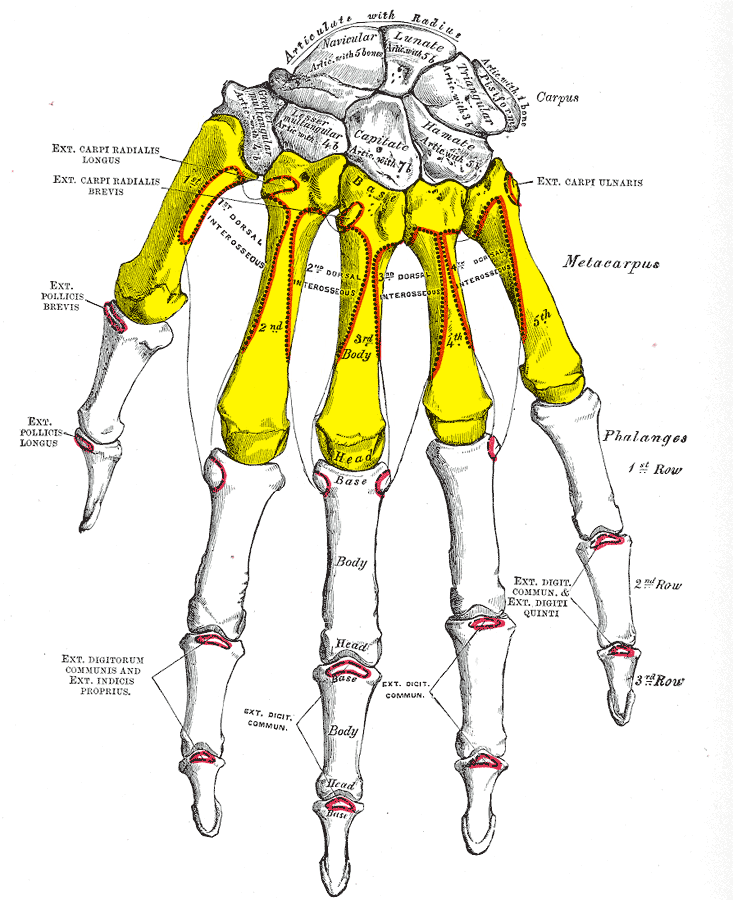
Base
The base (basis) or carpal extremity is of a cuboidal form, and broader behind than in front: it articulates with the carpal bones and with the adjoining metacarpal bones; its dorsal and volar surfaces are rough, for the attachment of ligaments.
Head
The head (caput) or digital extremity
presents an oblong surface markedly convex from before backward, less
so transversely, and flattened from side to side; it articulates with
the proximal phalanx.
It is broader, and extends farther upward, on the volar than on the
dorsal aspect, and is longer in the antero-posterior than in the
transverse diameter. On either side of the head is a tubercle for the
attachment of the collateral ligament of the metacarpophalangeal joint.
The dorsal surface, broad and flat, supports the tendons of the extensor muscles.
The volar surface is grooved in the middle line for the passage of
the flexor tendons, and marked on either side by an articular eminence
continuous with the terminal articular surface.
Neck
The neck, or subcapital segment, is the transition zone between the body and the head.
Articulations
Besides the metacarpophalangeal joints, the metacarpal bones articulate by carpometacarpal joints as follows:
- the first with the trapezium;
- the second with the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and third metacarpal;
- the third with the capitate and second and fourth metacarpals;
- the fourth with the capitate, hamate, and third and fifth metacarpals;
- and the fifth with the hamate and fourth metacarpal;
Insertions
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus/Brevis: Both insert on the base of metacarpal II; Assist with wrist extension and radial flexion of the wrist
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris: Inserts on the base of metacarpal V; Extends and fixes wrist when digits are being flexed; assists with ulnar flexion of wrist
Abductor Pollicis Longus: Inserts on the trapezium and base of metacarpal I; Abducts thumb in frontal plane; extends thumb at carpometacarpal joint
Opponens Pollicis: Inserts on metacarpal I; flexes metacarpal I to oppose the thumb to the fingertips
Opponens digiti minimi:
Inserts on the medial surface of metacarpal V; Flexes metacarpal V at
carpometacarpal joint when little finger is moved into opposition with
tip of thumb; deepens palm of hand.
Clinical significance
Congenital disorders
The fourth and fifth metacarpal bones are commonly "blunted" or shortened, in pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism.
A blunted fourth metacarpal, with normal fifth metacarpal, can signify Turner syndrome.
Blunted metacarpals (particularly the fourth metacarpal) are a symptom of Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
Fracture
The neck of a metacarpal is a common location for a boxer's fracture
The metacarpals
are long bones within the hand that are connected to the carpals, or
wrist bones, and to the phalanges, or finger bones. The metacarpals
together are referred to as the 'metacarpus.' The tops
of the metacarpals form the knuckles where they join to the wrist. On
the palm side, they are covered with connective tissue. You can feel and
see the metacarpals on the back of your hand, through your skin. The
five metacarpals are called thumb metacarpal, index metacarpal, middle metacarpal, ring metacarpal, and small metacarpal.
Ten percent of all fractures that occur are those to the metacarpals
and phalanges, the most common injuries being from car accidents, sports
injuries, and work-related injuries. The goal in repairing these
injuries is to do so while maintaining strength of hand grip and no
residual pain upon using the hand. Boxers tend to have high incidence of
fracture to metacarpals, hence the term 'Boxers Fracture.'
.

Post a Comment