ARTICLE ON ANATOMY OF THE UPPER LIMB (RADIUS)
INTRODUCTON
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The radius is shorter and smaller than the ulna. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.
The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone.
The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the tibia.
STRUCTURE
 The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone.
It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the
extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the
head.
The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone.
It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the
extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the
head.
The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are somewhat arched at the upper end and pass upward from the compact layer of the shaft to the fovea capituli (the humerus's
cup-shaped articulatory notch); they are crossed by others parallel to
the surface of the fovea. The arrangement at the lower end is somewhat
similar. It is missing in radial aplasia.
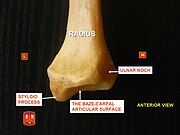
 The radius has a body and two extremities. The upper extremity of the radius consists of a somewhat cylindrical head articulating with the ulna and the humerus, a neck, and a radial tuberosity. The body of the radius is self-explanatory, and the lower extremity of the radius is roughly quadrilateral in shape, with articular surfaces for the ulna, scaphoid and lunate bones. The distal end of the radius forms two palpable points, radially the styloid process and Lister's tubercle on the ulnar side. Along with the proximal and distal radioulnar articulations, an interosseous membrane originates medially along the length of the body of the radius to attach the radius to the ulna.
The radius has a body and two extremities. The upper extremity of the radius consists of a somewhat cylindrical head articulating with the ulna and the humerus, a neck, and a radial tuberosity. The body of the radius is self-explanatory, and the lower extremity of the radius is roughly quadrilateral in shape, with articular surfaces for the ulna, scaphoid and lunate bones. The distal end of the radius forms two palpable points, radially the styloid process and Lister's tubercle on the ulnar side. Along with the proximal and distal radioulnar articulations, an interosseous membrane originates medially along the length of the body of the radius to attach the radius to the ulna.The distal end (Near the wrist)
The distal end of the radius is large and of quadrilateral form.
- Joint surfaces
It is provided with two articular surfaces - one below, for the carpus, and another at the medial side, for the ulna.
- The carpal articular surface is triangular, concave, smooth, and divided by a slight antero-posterior ridge into two parts. Of these, the lateral, triangular, articulates with the scaphoid bone; the medial, quadrilateral, with the lunate bone.
- The articular surface for the ulna is called the ulnar notch (sigmoid cavity) of the radius; it is narrow, concave, smooth, and articulates with the head of the ulna.

These two articular surfaces are separated by a prominent ridge, to
which the base of the triangular articular disk is attached; this disk
separates the wrist-joint from the distal radioulnar articulation.
- Other surfaces
This end of the bone has three non-articular surfaces - volar, dorsal, and lateral.
- The volar surface, rough and irregular, affords attachment to the volar radiocarpal ligament.
- The dorsal surface is convex, affords attachment to the dorsal radiocarpal ligament, and is marked by three grooves. Enumerated from the lateral side:
- The first groove is broad, but shallow, and subdivided into two by a slight ridge: the lateral of these two, transmits the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis longus muscle; the medial, the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.
- The second is deep but narrow, and bounded laterally by a sharply defined ridge; it is directed obliquely from above downward and lateralward, and transmits the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle.
- The third is broad, for the passage of the tendons of the extensor indicis proprius and extensor digitorum communis.
- The lateral surface is prolonged obliquely downward into a strong, conical projection, the styloid process, which gives attachment by its base to the tendon of the brachioradialis, and by its apex to the radial collateral ligament of wrist joint. The lateral surface of this process is marked by a flat groove, for the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus muscle and extensor pollicis brevis muscle.
Body
The body of the radius (or shaft of radius) is prismoid
in form, narrower above than below, and slightly curved, so as to be
convex lateralward. It presents three borders and three surfaces.
- Borders
The volar border (margo volaris; anterior border; palmar;) extends from the lower part of the tuberosity above to the anterior part of the base of the styloid process below, and separates the volar
from the lateral surface. Its upper third is prominent, and from its
oblique direction has received the name of the oblique line of the
radius; it gives origin to the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (also flexor digitorum sublimis) and flexor pollicis longus muscle; the surface above the line gives insertion to part of the supinator muscle. The middle third of the volar border is indistinct and rounded. The lower fourth is prominent, and gives insertion to the pronator quadratus muscle, and attachment to the dorsal carpal ligament; it ends in a small tubercle, into which the tendon of the brachioradialis muscle is inserted.
The dorsal border (margo dorsalis; posterior border) begins above at the back of the neck, and ends below at the posterior part of the base of the styloid process;
it separates the posterior from the lateral surface. is indistinct
above and below, but well-marked in the middle third of the bone.
The interosseous border (internal border; crista interossea; interosseous crest;) begins above, at the back part of the tuberosity,
and its upper part is rounded and indistinct; it becomes sharp and
prominent as it descends, and at its lower part divides into two ridges
which are continued to the anterior and posterior margins of the ulnar notch. To the posterior of the two ridges the lower part of the interosseous membrane is attached, while the triangular surface between the ridges gives insertion to part of the pronator quadratus muscle.
This crest separates the volar from the dorsal surface, and gives
attachment to the interosseous membrane. The connection between the two
bones is actually a joint referred to as a syndesmosis joint.
- Surfaces
The volar surface (facies volaris; anterior surface) is concave in its upper three-fourths, and gives origin to the flexor pollicis longus muscle; it is broad and flat in its lower fourth, and affords insertion to the Pronator quadratus.
A prominent ridge limits the insertion of the Pronator quadratus below,
and between this and the inferior border is a triangular rough surface
for the attachment of the volar radiocarpal ligament.
At the junction of the upper and middle thirds of the volar surface is
the nutrient foramen, which is directed obliquely upward.
The dorsal surface (facies dorsalis; posterior surface) is convex, and smooth in the upper third of its extent, and covered by the Supinator. Its middle third is broad, slightly concave, and gives origin to the Abductor pollicis longus above, and the extensor pollicis brevis muscle
below. Its lower third is broad, convex, and covered by the tendons of
the muscles which subsequently run in the grooves on the lower end of
the bone.
The lateral surface (facies lateralis; external surface) is convex throughout its entire extent and is known as the convexity of the radius, curving outwards to be convex at the side. Its upper third gives insertion to the supinator muscle. About its center is a rough ridge, for the insertion of the pronator teres muscle. Its lower part is narrow, and covered by the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus muscle and extensor pollicis brevis muscle.
Proximal end (Near the elbow)
The upper extremity of the radius (or proximal extremity) presents a head, neck, and tuberosity.
- The radial head has a cylindrical form, and on its upper surface is a shallow cup or fovea for articulation with the capitulum (or capitellum) of the humerus. The circumference of the head is smooth; it is broad medially where it articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, narrow in the rest of its extent, which is embraced by the annular ligament. The deepest point in the fovea is not axi-symmetric with the long axis of the radius, creating a cam effect during pronation and supination.
- The head is supported on a round, smooth, and constricted portion called the neck, on the back of which is a slight ridge for the insertion of part of the supinator muscle.
- Beneath the neck, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into a posterior, rough portion, for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii muscle, and an anterior, smooth portion, on which a bursa is interposed between the tendon and the bone.
Development
The radius is ossified from three
centers: one for the body, and one for each extremity. That for the
body makes its appearance near the center of the bone, during the eighth
week of fetal life.
Ossification commences in the lower end between 9 and 26 months of age. The ossification center for the upper end appears by the fifth year.
The upper epiphysis fuses with the body at the age of seventeen or eighteen years, the lower about the age of twenty.
An additional center sometimes found in the radial tuberosity, appears about the fourteenth or fifteenth year.
FUNCTIONS
Muscle attachments
The biceps
muscle inserts on the radial tuberosity of the upper extremity of the
bone. The upper third of the body of the bone attaches to the supinator, the flexor digitorum superficialis, and the flexor pollicis longus muscles. The middle third of the body attaches to the extensor ossis metacarpi pollicis, extensor primi internodii pollicis, and the pronator teres muscles. The lower quarter of the body attaches to the pronator quadratus muscle and the tendon of the supinator longus.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Radial aplasia refers to the congenital absence or shortness of the radius. Radial aplasia is a congenital defect which affects the formation of the radius bone
in the arm. The radius is the lateral bone which connects to the wrist
via articulation with the carpal bones. A child born with this condition
has either a short or absent radius bone in one or both of his or her
arms. Radial aplasia also results in the thumb being either partly
formed or completely absent from the hand. Radial aplasia is connected
with the condition VACTERL association.
Radial aplasia is not inherited. The cause for radial aplasia in
unknown, but it widely believed to occur within the first ten weeks of
gestation.
Fracture
Specific fracture types of the radius include:
- Proximal radius fracture. A fracture within the capsule of the elbow joint results in the fat pad sign or "sail sign" which is a displacement of the fat pad at the elbow.
- Essex-Lopresti fracture - a fracture of the radial head with concomitant dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint with disruption of the interosseous membrane.
- Radial shaft fracture
- Distal radius fracture
- Galeazzi fracture - a fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint
- Colles' fracture - a distal fracture of the radius with dorsal (posterior) displacement of the wrist and hand
- Smith's fracture - a distal fracture of the radius with volar (ventral) displacement of the wrist and hand
- Barton's fracture - an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint.


Post a Comment